Цитата:
Exercise 1.4.
(i) Construst a standard normal random variable
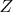
on the probability space
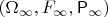
of Examlpe 1.1.4 under the assumption that the probability for head is
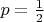
. (Hint: Consider Examples 1.2.5 and 1.2.6.)
(ii) Define a sequence of random variables
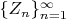
on
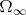
such that
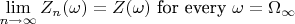
and, for each
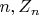
depends only on first
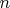
coin tosses. (This gives us a procedure for approximmating a standard normal random variable by random variables generated by a finite number of coin tosses, a useful algorithm for Monte Carlo simulation.)
Пример 1.1.4 я приводил на предыдущей странице 1:
http://dxdy.ru/posting.php?mode=quote&f=27&p=829551В примере 1.2.5 устанавливается следующая случайная величина с равномерной плотностью распределения:
Цитата:
For
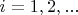
we define
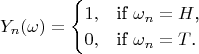
We set
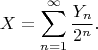
If
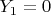
, which happens with probability
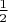
, then
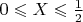
. If
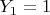
, which also happens with probability
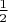
, then
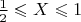
. If
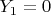
and
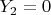
, which happens with probability
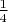
, then
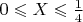
. If
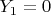
and
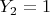
, which also happens with probability
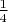
, then
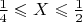
. This pattern continues; indeed for any interval
![$[ \frac{k}{2^n}, \frac{k+1}{2^n}]\subset[0,1]$ $[ \frac{k}{2^n}, \frac{k+1}{2^n}]\subset[0,1]$](https://dxdy-02.korotkov.co.uk/f/1/0/7/1075309d57b21b24da6a969b29167eaf82.png)
, the probability that the interval contains X is
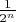
.
В примере 1.2.6 задается случайная величина с плотностью вероятности
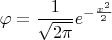
Можно попытаться сконструировать требуемую величину, как сумму выпадений "гербов" "H" и поделив ее на
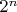
или
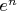
(или другую показательную функцию). Это верный ход?
Сумма выпадений
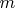
"гербов" из
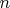
бросков определяется как
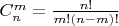
Я нашел в википедии следующую формулу для факториала (формула Стирлинга):
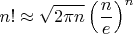
Может быть, здесь можно что-то получить преобразованиями?