Условие английское:
30-4. The spectrograph at the 150 ft solar tower telescope of the Mt. Wilson Observatory is of the Littrow type, shown schematically in the figure. In this instrument, a single lens acts as both the collimator and camera lens, and
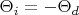
(nearly). The spectrum is formed in a strip adjacent to the slit. The focal length of the Mt. Wilson instrument is
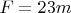
, and the grating has a ruled area
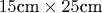
with
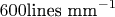
. The fifth order spectrum is commonly used.
a) At what angle
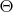
should the grating be tilted to bring the line
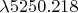
of neutral iron in coincidence with the entrance slit in the fifth order spectrum?
b) What other wavelengths in the range
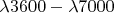
will also be coincident with the slit?
c) Suggest a simple way to remove the unwanted orders, leaving only the fifth order.
d) What is the dispersion of the instrument at fifth order
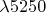
?
e) What is the minimum
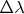
which can theoretically be resolved at fifth order
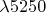
by this insrument?
Условие русское:
30.4. Спектрограф 150-футового солнечного башенного телескопа, находящегося в обсерватории Маунт Вильсон, показан схематически на рисунке. В этом устройстве одна и та же линза действует и как коллиматорная, и как камерная,
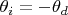
(почти!). Фокусное расстояние всего устройства
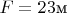
а решетка имеет площадь
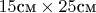
, причем в
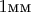
ее содержится
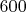
линий. Обычно при наблюдениях используется спектр пятого порядка.
а) При каком угле
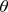
наклона решетки линия спектра возбуждения нейтрального атома железа, отвечающая длине волны
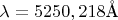
, будет совпадать с положением щели в спектре пятого порядка?
б) Для каких других длин волн в интервале от
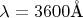
до
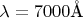
линия спектра также будет совпадать с положением щели?
в) Предложите простой способ устранения в наблюдаемой картине спектров нежелательных порядков, оставив только спектр пятого порядка.
г) Какова дисперсия рассматриваемого устройства при длине волны
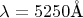
, отвечающей линии в спектре пятого порядка?
д) Каково минимальное теоретическое значение
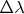
, которое может быть разрешено при длине волны
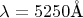
в спектре пятого порядка?
Интересует вопрос C). Согласно
секции 30-2 лекции 30 , добиться исключения спектров других порядков можно , сделав профиль дифракционной решетки несимметричным пилообразным. И якобы в таком случае получатся пары антенн с разной относительной фазой и разной амплитудой. Однако я не вижу , как разная амплитуда и фаза поможет избавиться от каких-либо спектров.
Допустим, имеем решетку, каждая линия является парой осцилляторов с суммарным полем:
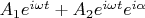
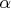
-- относительная разность фаз в каждой паре.
Для следующей линии:
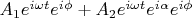
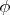
-- относительная разность фаз между соседними линиями.
Просуммировав по всем линиям, получим результирующее поле:
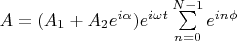
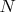
-- количество линий решетки.
Из лекции 30 известно, что последний множитель дает вклад в амплитуду
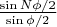
. Т.е. получаем 2 вектора с модулями
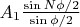
,
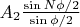
и с углом между ними
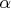
. Тогда результирующая амплитуда поля решетки запишется:
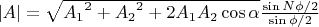
.
Это мало чем отличается от амплитуды поля решетки с линиями как единичными осцилляторами:
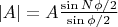
.
При тех же самых углах , которые соответствуют
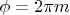
, где
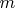
-- порядок спектра, -- будут наблюдаться максимумы. Интенсивность всех максимумов (а не отдельно взятого) будет зависеть от угла
.
В решебник пока не заглядывал, хочу понять, можно ли решить задачу с той информацией, что дана в лекции 30.